|
|
 |
| Formulation quantity |
The following equation and nomograph provide two ways to determine the appropriate
quantity of Duranate™ (in weight parts) for a given polyol, from the Duranate™ NCO, the
polyol quantity and OHV, and the desired NCO/OH ratio. |
|
|
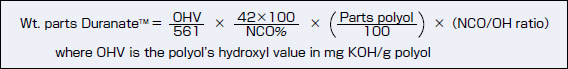
Example 1.
For Duranate™ TPA-100 (NCO = 23.1%), polyol having OHV=80, and NCO/OH = 1.0:
| Wt. parts Duranate™ = |
80×42×100
561×23.1 |
×(1.0)=25.9 |
|
|
To find the required Duranate™ quantity (in wt. parts per 100 wt. parts polyol):
 |
To find the required Duranate™ quantity (in wt. parts per 100 wt. parts polyol):Note:
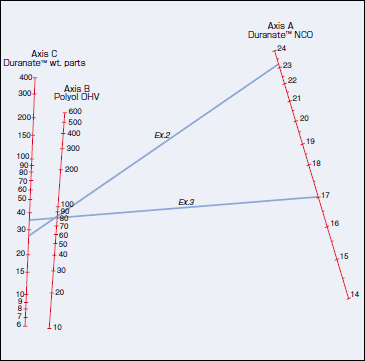
| (1) |
For a Duranate™ grade having NCO<14%,
use twice the actual NCO value in Step 1 and
then multiply the value on Axis C in Step 2 by
two, to obtain the required quantity for
NCO/OH = 1.
|
| (2) |
For a polyol having an OHV value outside the
Axis B range, multiply the actual OHV value
by an appropriate factor (fraction or integer)
to obtain an adjusted value within that range,
use the adjusted value as the OHV value in
Step 1, and multiply the value on Axis C in
Step 2 by the same factor, to obtain the
required quantity for NCO/OH = 1.
|
Example 2.
For the same materials as Example 1:
Extend straight line from 23.1 on Axis A
through 80 on Axis B to Axis C, and read the
value of approx. 26 on Axis C as the
Duranate™ quantity required for this
application, in wt. parts per 100 wt. parts
polyol.
Example 3.
For Duranate™ E402-90T (NCO = 8.5%),
with all other materials as in Examples 1
and 2:
Multiply NCO value by two, extend straight
line from 17 on Axis A through 80 on Axis B
to Axis C, read the value of approx. 35 on
Axis C, and multiply by two to obtain the
Duranate™ quantity of 70 wt. parts per 100
wt. parts polyol as the requirement for this
application. |
|
 |
|